Back to ACHIEVE Home Page
Back to Earth & Space Science Study Page
LESSON 31
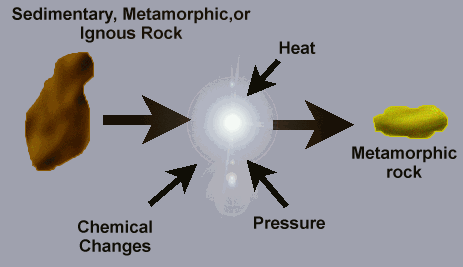
Mountains
PICTURE: ANYMOUNTAIN
The earth is a dynamic and constantly-changing planet. Oceans surge, weather rages, and land forms shift, uplift, and change with time.
It is the changing appearance of the land, as well as the formation of mountains and volcanoes that are the subjects of this lesson.
The earth's crust is composed of rocks that can change shape if they undergo enough stress. Compression, tension, and shearing all affect rock in different ways.

PICTURE: rockmor
Types of Stress
compression
tension
shearing
PICTURE: rkstcm
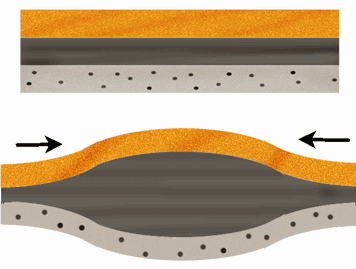
Compression
is the squeezing together of rocks. It results in rocks being pushed higher and deeper as the same amount of material tries to occupy less space.The collision of a continental plate and an oceanic plate results in compression, volcanism, and mountain formation.

PICTURE: conocnpl
When rocks are compressed, they form folds by bending without breaking. If the fold curves up, an ANTICLINE is produced. If the fold curves down, a SYNCLINE is produced. Folds may be large or small.
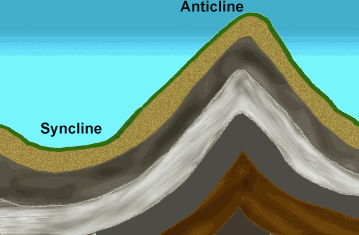
PICTURE: antsycln
When tension pulls crustal plates apart, the plate thins. This is because the same amount of matter is occupying a greater space.
Shearing
occurs when plates are pushed in opposite directions along a horizontal plane. Bending and breaking occurs because the same amount of matter is occupying the same amount of space, but in a different position.These three types of tensions can change the appearance of rocks by altering its shape or volume.
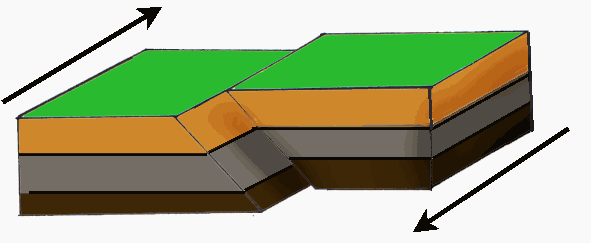
Tension or pressure from deep inside the earth can cause rock to break or FRACTURE. If the two rock masses produced by the fracture were to move, a FAULT results.
|
Fault Types |
|
normal fault reverse fault thrust fault strike-slip fault |
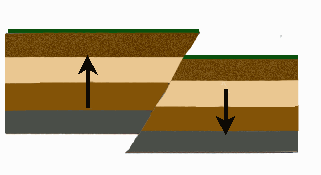
NORMAL FAULT
One block moves up and the other moves down.

PICTURE: norfault
REVERSE FAULT
Similar to normal fault but with overhang produced.
PICTURE: revfault
THRUST FAULT
One block slides over the other.
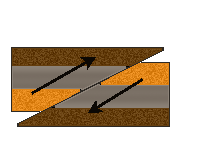
PICTURE: thrfault
STRIKE-SLIP FAULT
Also called a lateral fault; movement is horizontal in opposite directions.
PICTURE: strfault
Folding and faults are important because they produce mountains. Mountains are landforms elevated high above sea level. The difference between hills and mountains is their height. To be classified a mountain, the landform must be at least 600 meters higher than the surrounding landscape.
A mountain can be a single peak, part of a chain, or a range of mountains. Mountains can form under the ocean or on land. On land, they influence the climate and water availability to a region and provide habitat for plants and animals.
Mountains on land are an important source of natural resources, including minerals and lumber.
Mountains pass through three stages in the process of developing.
YOUNG MOUNTAINS are characterized by steep sides with jagged peaks and narrow valleys.
MATURE MOUNTAINS have weathered, rounded peaks and gentle slopes.
OLD MOUNTAINS exhibit flattened, rolling peaks and wide valleys.
PICTURE
Groups of mountains form ranges, which are also known as chains. A group of ranges comprises a mountain system. A group of mountain systems make a mountain belt.
Individual Mountain
Mountain Range
Mountain System
Mountain Belt
individual mountain
MOUNT BLANC
mountain range
WESTERN ALPS
mountain system
ALPS
mountain belt
EURASIAN-MELANESIAN BELT
Famous Mountains/Locations
|
Matterhorn
Mauna Loa
Mont Blanc
Mount Etna
Mount Everest Mount Fuji Mount Hood
Mount McKinley
Mount Rainier
Mount Shasta
Mount Olympus
Pikes Peak
Vesuvius |
A favorite for mountain climbers - Alps/Switzerland/Italy. This is the highest island mountain peak on earth, largest volcano in the world - Hawaii Highest mountain in the Alps - Alps/Switzerland, France, Italy This volcano has erupted more than 250 times - Sicily Highest mountain on earth - Tibet/Nepal This is a sacred mountain/Japan This mountain is covered with glaciers - Cascade Range/Oregon/United States Highest peak in North America - Alaska Range/Alaska/United States Highest peak in Washington and a tourist attraction - Cascade Range/Washington/United States Famous for having twin peaks - Cascade Range/ California/United States This mountain was considered to be the home of the gods in Greek mythology - Greece Famous mountain and site of many racing events - Rocky Mountains/Colorado/United States This is the only active volcano on the mainland of Europe. It completely buried the city of Pompeii with ash and cinders in 79 AD. The eruption was so severe that it altered the course of the Sarno River/Italy |
PICTURE: MT. ST HELENS
Mount St. Helens is a volcanic mountain located in the Cascade range in the state of Washington. This volcano erupted in 1980 causing tremendous property damage and several deaths. The cloud of ash it emitted exploded 12 miles into the air. It was the first volcanic eruption in the continental United States since 1921.
|
Major Mountain Ranges of the World |
|
Himalayas Urals Alps Pyrenees Rocky Mountains Adirondacks Cascades Grand Tetons Andes |
Major Mountain Ranges in North America
|
Adirondack Mountains Allegheny Mountains Appalachian Mountains Berkshire Hills Black Hills Blue Ridge Mountains Canadian Shield Cascade Range Catskill Mountains Coast Range Cumberland Mountains Great Divide |
Great Smoky Mountains Green Mountains Olympic Mountains Ozark Mountains Rocky Mountains Saint Elias Mountains Selkirk Mountains Sierra Madre Sierra Nevada Teton Range White Mountains |
|
Major Mountain Systems in the World |
|
Appalachian Mountains Rocky Mountains Pacific Mountain system Andes Mountains Tethyan Mountain System Alp Mountain System Himalaya Mountain System |
Mountains differ in many ways, including the way in which they were formed. There are various processes that can cause mountain formation. Each process results in a particular type of mountain.
Types of Mountains
folded mountains
fault-block mountains
dome mountains
FOLDED MOUNTAINS
form when compression causes rock layers to bend and fold, but not break. This happens when crustal plates collide. Buckling occurs and folds result.PICTURE: rockfold
FAULT-BLOCK MOUNTAINS
form by vertical fault movement. Normal faults cause the formation of fault-block mountains. A block of crustal plate rises up, while blocks on either side of it slide down.
PICTURE: fltblkmn
A RIFT VALLEY
is the reverse of a fault-block mountain. It forms when a wedge of coastal plate drops down between two blocks.PICTURE: riftvall
DOME MOUNTAINS
are formed from pools of magma that accumulate beneath the surface of the earth. They push up on the crustal plate and result in the formation of a domed mountain. This is not a volcano, because the magma does not reach the earth's surface.Plateaus
Plateaus have been described as mountains with flat tops. They are elevated land forms that are flat rather than peaked.
Plateaus form when huge areas of the crust are pushed upward.
Plains
Plains are large flat areas of land. They are not elevated land forms, but are found fairly close to sea level. There are two type of plains: coastal and interior.
Coastal plains are found near coastal areas and interior plains are found in the interior of a land mass.
A coastal plain is a section of lowland that extends along a seacoast. The plain may have been below sea level at one time in history and been part of the continental shelf.
An interior plain is a flat stretch of land that extends for many miles without any noticeable changes in elevation. Interior plains may occur at any altitude.
Plains are usually composed of grasslands, which makes them good for farming. The soil is normally rich, and rainfall is usually adequate.
In the United States, the Great Plains area is called "The Breadbasket." This refers to the fact that most of the United States' grains and foods are produced in this region.
This area is also used for production of beef cattle, dairy cattle, hogs, and sheep. The grassland makes excellent grazing for these animals. Farms and ranches cover the Great Plains region.
Plains are located all across the globe. In South America, they are known as pampas and the cowboys who work on them are called gauchos.
In Africa, there is a huge plain called the savannah. It is well known as a home for much of Africa's wildlife. In southeast Europe and Asia, the plains region is known as the steppe.